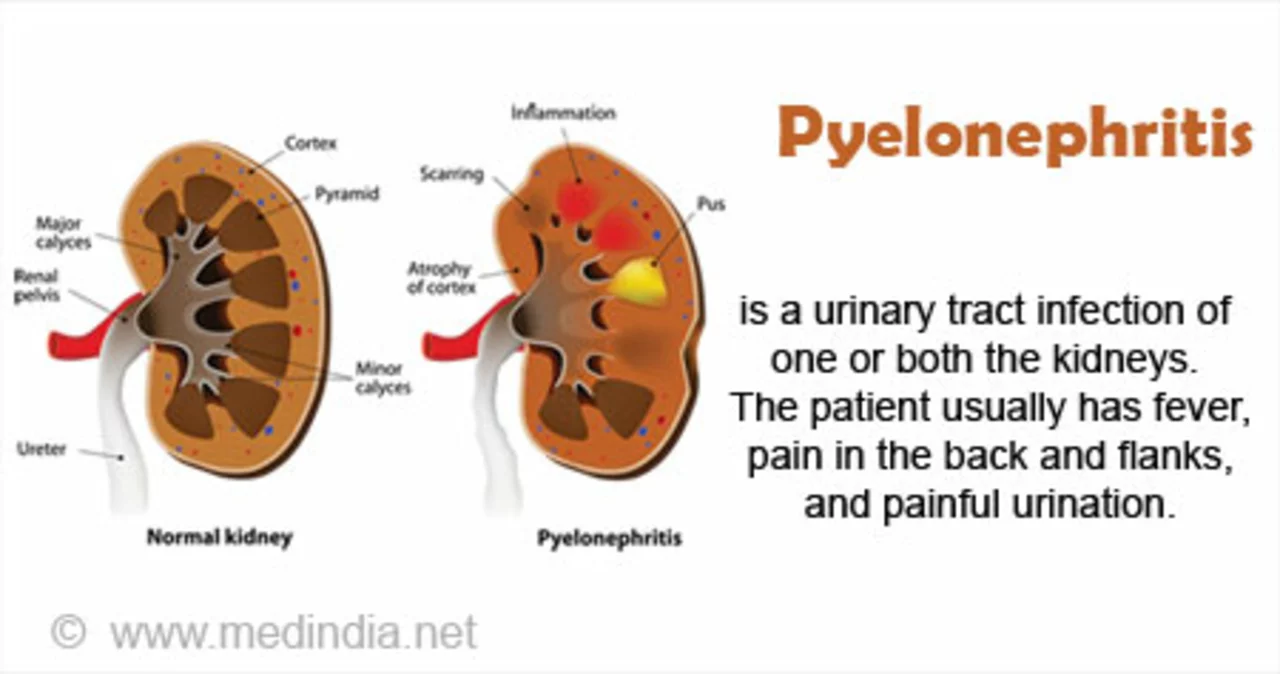
Understanding Pyelonephritis and Its Symptoms
Pyelonephritis, commonly known as a kidney infection, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects one or both kidneys. It's important to be aware of the symptoms associated with this condition, as early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications. Common symptoms include fever, chills, back or side pain, frequent urination, a strong and persistent urge to urinate, and cloudy, dark, bloody, or foul-smelling urine. If you suspect that you might have pyelonephritis, it's crucial to see a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
Azithromycin: An Antibiotic for Treating Pyelonephritis
Azithromycin is a type of antibiotic belonging to the macrolide class. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria, making it an effective option for treating various bacterial infections, including pyelonephritis. Azithromycin is often prescribed when other antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones or cephalosporins, are not suitable or have not been effective in treating the infection. Your healthcare provider will determine the best course of treatment based on your specific situation and the severity of your infection.
Proper Dosage and Administration of Azithromycin
It's essential to follow your healthcare provider's instructions when it comes to the dosage and administration of azithromycin for pyelonephritis. The medication is typically taken once daily, either with or without food. However, taking it with food may help reduce stomach upset. It's crucial to take azithromycin for the entire duration prescribed by your healthcare provider, even if you start to feel better before finishing the medication. Stopping the antibiotic too soon may lead to the infection returning or becoming resistant to the medication.
Possible Side Effects and Interactions
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with azithromycin. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and headache. If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, it's essential to contact your healthcare provider. More severe side effects, such as hearing loss, severe dizziness, or a fast or irregular heartbeat, require immediate medical attention.
It's also important to be aware of potential drug interactions. Some medications can interact with azithromycin, potentially reducing its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider of any other medications, supplements, or herbal products you may be taking to avoid any possible interactions.
Monitoring Your Progress and Recovery
While taking azithromycin for pyelonephritis, it's important to keep track of your symptoms and progress. This can help ensure that the medication is working effectively and that you're on the right track to recovery. If your symptoms do not improve within a few days or worsen, it's crucial to contact your healthcare provider for further evaluation and possible modification of your treatment plan. Remember that completing the full course of antibiotics is crucial for a successful recovery, even if you start to feel better sooner.
Preventing Pyelonephritis: Tips for a Healthy Urinary Tract
While azithromycin can be an effective treatment for pyelonephritis, prevention is always the best medicine. There are several steps you can take to maintain a healthy urinary tract and reduce your risk of developing a kidney infection. These include drinking plenty of water, urinating frequently and not holding it in, wiping from front to back after using the toilet, and practicing good hygiene. Additionally, women should avoid using irritating feminine products, such as douches or scented powders, which can increase the risk of infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you suspect that you have pyelonephritis or are experiencing symptoms consistent with a kidney infection, it's vital to seek medical attention promptly. Delaying treatment can lead to serious complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis, a life-threatening infection that can spread throughout the body. By being proactive and seeking appropriate care, you can help ensure a swift recovery and reduce the risk of long-term health issues.

Written by Guy Boertje
View all posts by: Guy Boertje